
Elon Musk’s Starship spaceship is an amazing ship that Elon has built on his own dime. Recently NASA has bought a single mission for $53 million to fund a refueling mission in space to demonstrate refueling a ship before sending it on to a longer objective.
The refueling will take place using 2 starships. One will refuel the other by a momentum method where small acceleration will shift the fuel. This is a pretty important maneuver because future missions will not carry all the fuel they need. They will be carrying cargo as much as possible.
They have also reportedly won a $2.9billion deal to take man back to the moon in a program called Artemis. Artemis will supposedly take man in 2024/5 or later.
There is no doubt Starship is Elon’s biggest achievement maybe that he will achieve in his life. It revolutionizes everything about space travel and I don’t think many people have grokked the full import of the transformation which spaceship will bring to space.
Nothing comes close or achieves comparable statistics ever made. It lifts more, bigger, costs less and is more capable in every way than any rocket or combination of rockets have ever been.
Like Tesla the industry will take decades to catch up. This rocket could easily become a virtual monopoly of space travel in 2023 or after.
Elon continues to refine starship dramatically. Most of the work is happening in Boca Chica Texas.
Just last week testing for the newest version engine of the starship named raptor started testing. This second version tested at peak output of 330 bar which beat any engine ever tested before anywhere in the world ever. Raptor 2 is being built to produce 300 bar or 250,000 lbs of thrust consistently for minutes. It is by far the best most powerful and flexible rocket engine ever produced.
At least 32 of these massively powerful engines will be clustered on the first stage of starship. The second stage is planned to have 9 of them enabling the second stage to take off from Mars.
SpaceX is also testing the gantry reusable recovery feature which will literally catch a returning starship as it lands to bring it into place where it can be refueled for liftoff 1 hour later.
Here are some comparative specs to the biggest rockets ever made for the Spaceship, Shuttle, Apollo and another rocket NASA is funding called SLS.
As you can see Starship is by far the most powerful with a lift thrust 50% greater than any rocket ever built previously. It will also be able to hold a payload 67 feet in length and near 30 feet diameter. This is greater than the capacity of the retired space shuttle.
- Height Apollo 363ft, Shuttle 184ft, SLS, 322ft, Starship 354ft
- Width Apollo 33ft, Shuttle 100ft , SLS 27 ft, starship 30ft
- weight 6.5 M lbs, shuttle 4.5 M lbs, 5.75 M lbs SLS, starship 8.5 M lbs
- Thrust. Apollo 8M lbs, Shuttle 7.5M lbs, SLS 8.5M lbs, Starship 12.7M lbs
- lift to LOE, Apollo 140kg, Shuttle 150kg, SLS 143kg, Starship 150kg
- reusable: Apollo :NA, Shuttle 7 month turnaround: reusable, SLS: NA, starship 2 hr turnaround: reusable
- Cost/mission : Apollo $1.23 B, Shuttle $2.0 B, SLS $5.0 B, starship $0.1 B
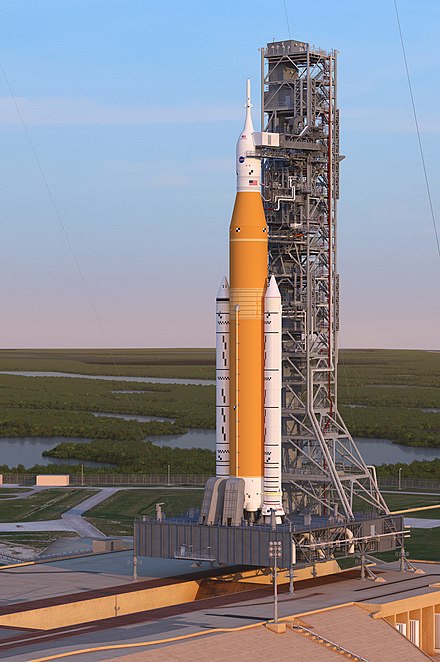

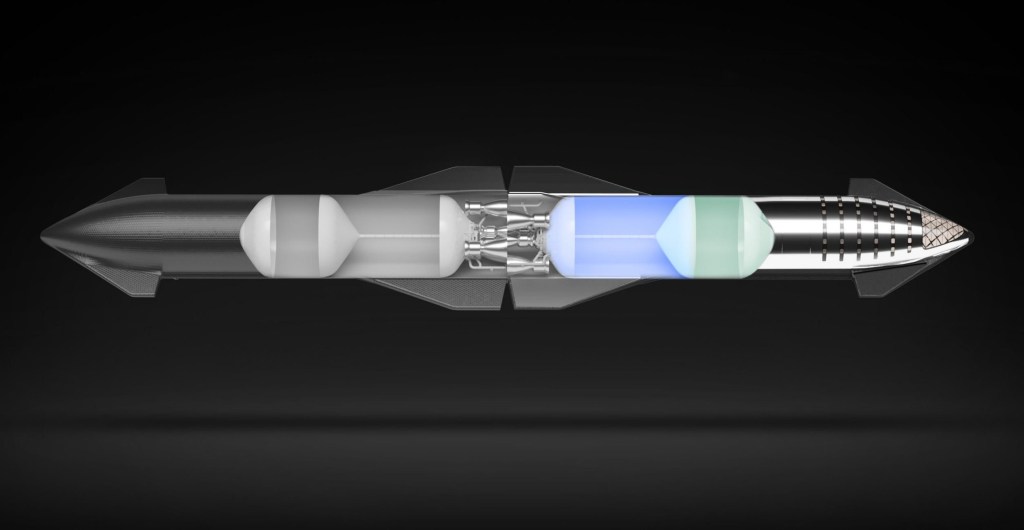





The biggest difference between these other rockets is the starship is totally reusable. Starship achieves reusability with amazing efficiency. Of course Apollo was 1960s technology and isn’t made anymore and probably couldn’t be made.
Boeing is trying to recreate Apollo with a program called the SLS that NASA is spending $4.2 billion on. So far it is way way way behind schedule over budget and is not reusable but resembles the cost characteristics of Apollo but worse. An SLS launch is estimated at $5 billion cost compared to Starship at $0.1 Billion. I assume SLS will be cancelled. It’s absurd. Why would we pay 50 times more for the same thing? So I won’t even entertain discussing it.
One of the reasons SLS is so inferior to Starship is that it uses solid rocket boosters like the shuttle. These boosters are not reusable and represent additional complexity like with the shuttle even if they could find a way to make it reusable. Spaceship was designed for incredible reusability learning everything that spaceX learned from Falcon. As a result SpaceX believes they can achieve LOWER cost per flight than falcon which is stunning considering its far higher lift capacity and size.
Starship is divided into 2 stages. Both stages can return to earth to be reused. This was a dream of NASA for years shuttle never achieved. A shuttle was actually 2 times more expensive to launch than the Apollo and 200 times more expensive than Starship.
The key to the efficiency is not having to use “pica” the material we have used on all returning spacecraft for decades. Pica is expensive and burns off each time. The constant replacement of pica is very expensive and problematic because if it doesn’t stay on it could cause a burn through and the ship could be destroyed. The replacement of tiles on the shuttle made the time to reuse very long. While pica is amazing substance that has been used on virtually every spaceship it is problematic.
Elon avoided using pica by choosing a radical design using steel. That’s right, good old steel. This was something NOBODY else considered like his revolutionary Falcon with landing rockets that nobody even considered before.
Steel has very high melting point. Elon is betting that the steel combined with a cooling layer of liquid circulated under the steel and carefully controlling the flight path on return will enable him to avoid the need to use pica. Not using pica essentially reduces costs, time to put back in service dramatically.
We will see if this is true possibly as early as next month. A full 2 stage starship will take off and go to earth orbit. The 2 stages will return with the upper stage to come in belly first and go through the re-entry at close to full speed to test the heat shield. This will be the first test of both stages combined and the heat shield.
Elon plans to dump the starship into the ocean and not planning to land it like subsequent missions but undoubtedly they will recover it to see how the rocket held up under the 3000 degree heat of re-entry without pica. They will collect data and refine the system in subsequent launches. Key to that will undoubtedly be to see if the steel / liquid cooled belly will indeed survive and work or what changes need to be made.
Mechzilla
Another kind of sci-fi feature of starship is that the 1st stage will return to the same structure it took off from. When it comes in to “land” two giant crane arms of steel will close in on the rocket as it slides back into the same place it took off from. The arms will grasp the rocket to stabilize it in case it doesn’t land perfectly. This will allow fast turnaround. Elon is projecting eventually having a 1-2 hour turnaround.
Elon calls the metal arms which will catch starship on its return trip mechzilla or something like that. This will be amazing to see but we won’t see mechzilla in action until later in 2024. However, the launch tower already has the arms built.

Another critical feature of Starship is the phenomenal performance of the raptor engine that is planned and already tested several times. There will be 32 of these engines at the base of the Starship. These engines have the ability to run in space, be refueled and operated many times.
The combined force of the raptor engines will easily exceed ANY spacecraft ever built. Generating 12.7 million lbs of thrust it will be 50% bigger than Apollo. This is an amazing vehicle that will blow our minds away when we see it in full glory.
Elon has said recently that the raptor engine is the biggest stumbling block in the project. He lost several key engineers that were designing and building them to competing space companies believe it or not. He says the production of these raptor engines could literally bankrupt SpaceX. I am not sure how it could do so but apparently there are production problems. They are very complex engines but he has already tested them many times on numerous test flights and test firings.
Last week saw raptor 2.0 tested. Not only did the engine achieve the 300 bar mark required for starship but it is vastly more buildable than raptor 1. The piping and wiring was simplified

The raptor engines of which there will be 32 on the first stage and 9 on the second stage are revolutionary in themselves. They are the highest performance engines I have researched in production. They generate a specific impulse of 380s, they produce lift to weight of 300 to 1. The RS-25 used on SLS produces 363 specific impulse.
Raptors operate on methane and liquid oxygen. This was chosen as the fuel because it is easily made on the moon and Mars. The idea of refueling Starship in remote places was a key design. This is really designed to land on Mars and take off again.
A different configuration of the same engine is used in the 2nd stage with a longer bowl for more efficient delta V in space. The efficiency of a rocket engine is dependent on forcing the ejected material as straight out the back as possible for maximum momentum gain. In atmosphere such large bowls don’t work as well.
In all these ways the Starship is truly a phenomenal innovation in space launch that makes even the falcon look old fashioned.
The Starship also has a science fiction look because it is made of what appears to be silver it looks absolutely beautiful. It is hard to overstate how fucking crazy this is.
Here are the key revolutionary features of Starship:
- Many times Reusable with 2 hour turnaround eventually planned
- Nondestructive heat shield
- Methane engines with incredible thrust that can operate in air or vacuum.
- Starship can be refueled in space from another Starship or from the Moon and Mars using fuel manufactured indigenously.
- The ability on re-entry to be captured by a giant arm system to allow virtually instant turnaround.
- Phenomenal 122 foot potential faring for large payloads and enormous lift potential to LOE or GS orbit.
- The ability to do powered landing on Mars or the Moon without parachutes or other complicated mechanisms unlike previous ships
- The ability to refuel and take off from remote planets.
This set of features makes science fiction writers dreams come true.
This rocket can do it all. It can lift huge quantities into space cheaply (50 times cheaper than we have in the past), be refueled in space to continue journey to distant planets. Be refueled on planets like Mars and the Moon and take off and land vertically on other planets.
If can go to farther destinations faster than any conventional program and take vastly more mass with it.
Taking more mass means being able to create depots of fuel or supply items that can be used by subsequent Starships for longer missions.
Imagine you want to go to Jupiter. You can prestage supplies along the way so that your final mission you visit these to have enough fuel and supplies without having to carry them with you initially.
Today we are limited to 1,000 lbs for most missions that go beyond the orbit of the earth. Starship raises this to 150,000 lbs.
Not only that instead of using gravity assist orbits that take years to traverse the solar system and planning decades in advance for these tricky very precisely planned missions that leverage rare orbit tricks to minimize fuel but take years to traverse.
Starship can use rocket power to make brute force delta V sufficient to get to other planets in many more timely direct paths and much faster.
Starship could even have refueling Starships in orbit around or along the way to Jupiter for instance to provide much more flexible missions. With Starship we could plan manned missions to Jupiter. Not as theoretical but very practically using off the shelf technology.
In other words Statship is the thing that sci-fi dreamers have hoped mankind would achieve at some point so that we could do the crazy things that they write about.
Starship can be utilized for many missions to transport people around the solar system not just the Moon or Mars. Provide enough capacity to build resupply stations around the solar system to facilitate longer missions and faster returns or deeper missions.
When compared to the Boeing SLS program, Shuttle or Apollo or anything else even planned by any other country it is a joke. Starship is a ship that enables dreams and is economical to accomplish those dreams.
The SLS is a large rocket that could do some of the things Starship could but because of its fantastically higher cost it would make many ideas I just postulated absurdly expensive. Starship not only makes these missions possible it makes them affordable which means they are truly not just fantasies.
Maybe this is one reason why Elon recently cashed out 5% of his Tesla stock raising $10 billion in cash. I wouldn’t be surprised to see him commit billions to Starship or the programs he is planning.
What an amazing thing that this kid from South Africa who dreamed of building rockets to inspire NASA to do more is not only able to build rockets but have enough money himself personally to fund missions to Mars if he wanted.
He is driving the cost so low to enable doing things that are dreams right now.
So, presumably he’s not building it and then sitting around with it waiting for others to come up with dreams. He must push those dreams to use his fabulous creation.
The key variable in all plans of doing anything in space comes down to the cost to lift a lb out of the gravity well of the Earth. Elon has achieved an unbelievable factor of 400 reduction from the Shuttle. This means that much bigger plans can be imagined. Let’s imagine those plans because they are not crazy now.
When you consider his main competition is Boeing’s SLS which is expected to cost $5 billion per mission it is a little hard to fathom how NASA spends another penny on the delayed and ridiculous program.
Elon plans to use starship to go to mars but starship changes the formula for all space travel because of the cost factor.
Should Elon go to Mars by himself?
Elon built this amazing craft. So far, the world has not responded with missions to use this technology. Maybe Elon himself should help spearhead these much larger space plans? I would be surprised if he didn’t.

NASA’s current plan is to go to the Moon by 2024. The program is called Artermis. It is funded for $2.9 billion. The moon is only marginally interesting. I will talk about Moon missions later in this blog.
Elon could propose to go to Mars by himself and use his money to launch spacecraft to go there. If he is incredibly economical he might be able to do it for $10 billion but he wouldn’t’ be able to start a colony.
To develop the robots and different things, supply and buildings for a colony is really a $50-250 billion plan. Given that he’s worth a trillion he might be able to do it but he’d have to liquidate his ownership in Tesla entirely.
Going to Mars is one thing. Going to Mars and living there means development of lots of other technologies and stuff. It means many missions. The cost starts to get to “beyond Musk” level. Besides why should he do it alone? He’s not the only one interested in man becoming more space faring and space exploring.
Elon’s original idea was to stimulate NASA to do more. It is long time past NASA getting the hint. They need to think and propose much bigger plants and work with Elon much more.
NASA probably can’t save much on trashing the SLS now. The money is probably already committed. Still I see no reason to build it further. I think it is a distraction besides any money put into it a waste. NASA wants to have 2 vendors to depend on. Fine. They should consider possibly one of the other private companies or get Boeing to redesign SLS along Starship directions or NASA should come up with some way they can license the technology from SpaceX and run a version of Starship on another branch they also fund.
However, the spacecraft themselves are only part of whatever missions we plan. They are the enabling technology that allows us to put the actual stuff we want to do in space where it needs to be economically. Elon has done that part. NASA’s job now is to imagine how to use Starship to do things Elon hasn’t funded.
If NASA won’t get up its collective testosterone and come up with plans I have an alternate plan for Elon. Go to other countries.
Let’s say Elon went to Europe and said: Help me fund missions to Mars. I will split the cost with you. You could spurt past the US and NASA and make Europe the leading space power.
He could go to China and do the same. Help me fund missions to Mars.
If he started to even hint he was looking for these kinds of help my guess is that NASA and the US would have to respond with a plan to do colonization and fund it or other programs to keep Elon’s attention.
The US cannot be in the position of being the second to Mars or to be behind in space. We would have to respond. I hope we respond and that we are not so pre-occupied with covid and racism and bullshit ideas like global warming that we can no longer do things like this anymore.
To me if the US abdicates this all the talk about America descending to 3rd world status is proved. When we have lost the ability to dream and get beyond these stupid and ridiculous petty political crap the democrats come up with and do real things again then America is truly gone.
Maybe Elon even hinting he would go to other countries would result in a joint thing where China, Japan, Europe contribute to this colonization effort or other large scale space effort I describe below maybe America leads a coalition if it doesn’t have the balls to do it itself.
We built the ISS with international cooperation. While in theory this sounds good the extra cost, time delays and lack of real funding by most of these other countries means they are hardly worth the effort.
It is not a ridiculous idea nor expensive to do many of these things I will talk about below. These countries could easily afford the cost of a reasonable Mars colonization effort especially along the lines I suggest using robots and not sending man. We could also in coordination with other countries do many of the things I describe below maybe some in conjunction with other countries.
I put this here in the article to spark interest in the idea that Elon could have private conversations to drive things forward using the combination of his own ability to fund things and threats using other interested parties to force a path forward.
Elon if you are interested contact me. Would be glad to strategize and help. But it will take a long time to get other players including NASA to start going in the right direction. The time to start pushing is now.
Let’s build new Space Stations
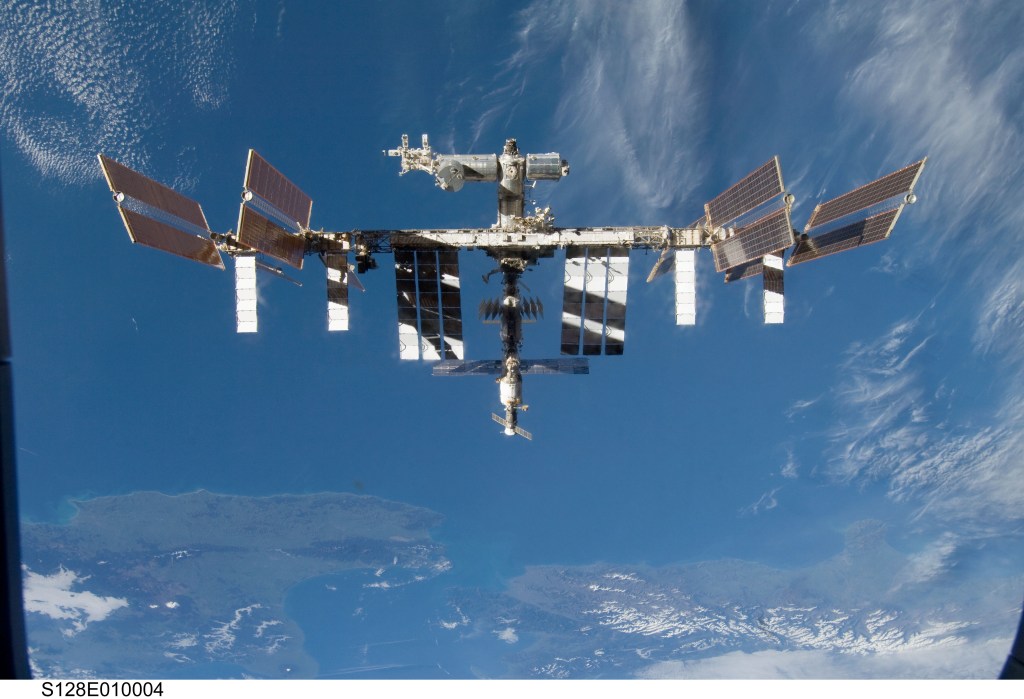

Starship enables us to consider multiple plans simultaneously. Maybe we go to the Moon, Mars and we build a new Space Station, a super telescope, bases on other planets.
We could build a Space Station that is 20 times larger than the ISS for 1/4 the cost of the ISS. It would be rotating and people could live on it for long periods of time safely.
Why build a new space station? What’s wrong with the ISS?
We put up the ISS over 10 years and 30 missions for a cost of $100 billion. It is 30 years old. It is likely the most expensive space project ever attempted. The foreign contribution was maybe 10% of the cost although originally it was planned to be more “joint” than it turned out.
Even the international components were shipped via shuttle which cost more than $2 billion per mission dwarfing in many cases the cost of the components being shipped.
The ISS Space station is about 4000 sq ft in area comprising 5 sections. It orbits in a relatively low earth orbit of 205 miles. Space is said to start somewhere around 100 miles. The ISS has to be lifted occasionally to keep it from falling to close to the earth or moved to avoid space debris from other missions.
The total cost to operate the ISS is $4 billion / yr out of a NASA budget of $20 billion.
Using Starship we could build ISS for a few billion in my opinion or pennies on a dollar compared to the cost back in the 80’s and 90’s.
New technology frequently makes things cheaper to do. That’s why it makes sense to put off trying to solve some problems till the technology is better, for instance, global warming. Solving global warming is not as Bloomberg has said primarily a political problem. It is an economic / technological problem. Until the technology to produce reusable energy is cheap enough we are pushing a rock up a hill trying to solve this. When solar and other alternatives are technologically solved better they will happen without even trying. That’s how the market works. We should focus on the technology.
Space technology could be a great impetus to building better energy technologies. But even if not the point is building a space station today is vastly cheaper and easier than in 1980. Literally probably 100 times cheaper.
In my opinion the ISS is highly underutilized to the point that it should either be mothballed or made part of some much larger project / set of projects which can justify it.
I think NASA should sell ISS to SpaceX to use for commercial purposes and to foster bigger projects discussed below.
Why a rotating space station is critical?

There is a more fundamental problem with the ISS. It is not rotating.
In the movie space odyssey 2001 Arthur Clarke proposed there would be a rotating space station in 2001. It’s 2021 and the ISS doesn’t spin. This may seem like a minor thing but in fact living on a space station is a deadly thing today. Staying for 6 months or longer puts your life in danger from atrophy.
Astronauts work out and try to stay fit on the ISS but nothing compares to the load gravity puts on the body to keep everything working properly. Even the most fit astronauts after 6 months suffer severe problems. If we plan longer missions in space to Mars or other planets we will have to deal with the issue that long term zero g is not good for the body.
While zero-g is associated with the romantic idea that seems associated inextricably with space it is an environment that causes naseau for a lot of people and is very inconvenient in a lot of ways. It takes a long time to become productive doing things in zero-g and there is danger that any liquid can float into electronics. Excretion is uncomfortable and complicated.
Maybe zero-g is cool for some experiments or to experience but for practical purposes it is counterproductive. We have always imagined we would need to produce artificial gravity. We need to do this.
If all you do is send a couple people a year into space maybe zero-g is fine but the long term problems of no gravity are serious. Eventually travel to any distant place like Mars will be vastly more problematic without gravity along the way. Sending lots of people into space will be difficult. A lot of people find zero-g very uncomfortable.
It also doesn’t need to be exactly 1g. We don’t know what level of gravity is good enough to provide enough force for the human body to stay in shape and to facilitate long term health. We hope we don’t need more than 0.3g because this is the gravity of Mars. We need to do experiments to determine this.
If we need to build rotating craft for travel to farther distances in the solar system to mars and beyond then we need to get some experience building rotating structures in space and building a space station would be an obvious first step.
Maybe the starship becomes the booster for a habitat for Astronauts that rotates on the way to Mars. That is not currently in the plans but if we get good at figuring out how to build these rotating structures I don’t see why that wouldn’t be natural and simple.
Fortunately, because of the economics of the starship building a space station that is 10-100 times larger than the ISS and rotates is eminently practical. The size of a new space station is a very interesting question.
Ideally the size would be enough so that when the people are rotating they don’t feel Coriolis forces which could become uncomfortable. The larger the diameter of the station the less likely people will find the rotation noticeable.
Since the area of the station is roughly say 25 feet (the width of the modules that make up the ring) X 2 X PI X R (the radius of the wheel) This assumes we have modules along the entire length of the wheel of the space station.
This area for a 500 foot radius space station with modules that are 25 feet wide and 12 feet height = 80,000 square feet of space or 960,000 cubic feet or more than 20 times the space of the current space station. That’s big. That’s like a building with 5,000 Sqft floors that is 16 stories tall.
That size space station is large enough to hold a population of 100 people with living space, work space and even areas for recreation and a mall, hotels, etc.
That would be incredible and is probably too big for anything we plan now but we could design it to ultimately be that big and simply put up modules as we can afford them so the entire round circumference wouldn’t be filled in initially but filled out over time.
A lack of uniformity of the placement of modules will be a problem as it will create instability in the rotation. Instability will cause us to have to use a lot of fuel to keep the station rotating in a non-disturbing way. We will have to balance the mass around the wheel almost perfectly to prevent it from wobbling and tumbling in very uncomfortable and dangerous ways.
The mass of an 960,000 cubic foot space station would be something like 5 million kg. That’s about 30 starship launches which isn’t outrageous. The cost of the lift would be somewhere around $3 and $5 billion which is 1/10 the cost of the original ISS but producing a space station that is 20 times bigger.
Of course the cost of the station would be considerably more than $3-5 billion for the lifting. There would be the structures that compose the stations, the design and the construction of it on land or in space.
A space station of radius r and angular velocity of w would produce a gravity of w^2 / r / 31. Thus a 500 foot radius station traveling at 70 foot/sec would produce a centripetal acceleration that feels like gravity of about 1/3rds Earths gravity. Which is 48 miles per hour.
A 500 foot radius station has a circumference of 3000 ft (a little over half a mile) which means the station would make one full rotation in 43 seconds. This is probably the smallest size and would produce noticeable psychological effects which would might take some time to get used to.
It is imagined in most visions of rotating space stations that there might be different modules at different distances from the center that would provide different gravities. So, there might be some labs at lower height for experiments or work that would benefit from lower gravity or don’t need higher gravity. Power systems and other life support functions probably can function with low gravity and not use the space at the higher levels which could be dedicated to human occupation.
In my mind the biggest problem with a rotating space station is keeping the thing balanced. Possibly a set of movable weights could be placed somewhere along the circumference that would move automatically to compensate for instabilities in the mass at different parts of the outer ring. With very precise accelerometers we have today it should easily be possible to design a fast response system that could keep the station in perfect rotation without having to use fuel.
The 500 foot radius circular living area 25 feet wide and 12 feet tall would accommodate reasonable living accommodations, hotels, equipment for maintenance of the living environment, production of energy, computer and communications systems.
Docking modules are usually located at the center of the station to minimize the difficulty of conjoining.
The space station could serve many functions.
- Tourism
- International cooperation
- Scientific experiments on a much grander scale
- Preparation for larger space missions including construction activities
- Storage space for supplies for space missions
- Processing of materials acquired from the moon, mars or asteroids prior to delivery to Earth
The current ISS weight is 2100sqft / 140,000 kg. It is very dense and I’m sure we can do less than half that but assuming this ratio still results in a weight of 12 million lbs. The current ISS is < 1 million lbs with 4,000sqft.
The cost of such a station could be anywhere between $10 billion for a minimal design up to $25 billion for a pretty robust station with lots of features like nuclear reactors for energy, multiple robotic arms for construction, extra storage modules for storing extra supplies for loading onto multiple docked starships. Experiment modules.
Instead of 7 people on the space station a 960,000 cubic foot space station could support a community of at least 100 or more people who would be operating in an environment with mars gravity and at least 3 times as much space per person as the current ISS.
It would take approximately 40 missions to put up all the modules. B
I would like to point out that the cost of this is significantly less than the original ISS cost for literally 20 times more space and functionality.
This is possible because of the capacity and economics of the Starship.
Where should the space station be located?
The current location of the ISS is low earth orbit. It might make sense to locate the new space station at geostationary orbit which is at 23,000 miles above the Earth. Objects located in geostationary orbit stay constant above a point over the earth.
Doing that affords much higher stability that wouldn’t require the constant adjustments of height the current ISS has to undergo. However, travel to geostationary orbit is far more energy intensive than getting to Low Earth Orbit where the ISS is located. Possibly the current ISS could be used as a transit stop on the way to the larger space station.
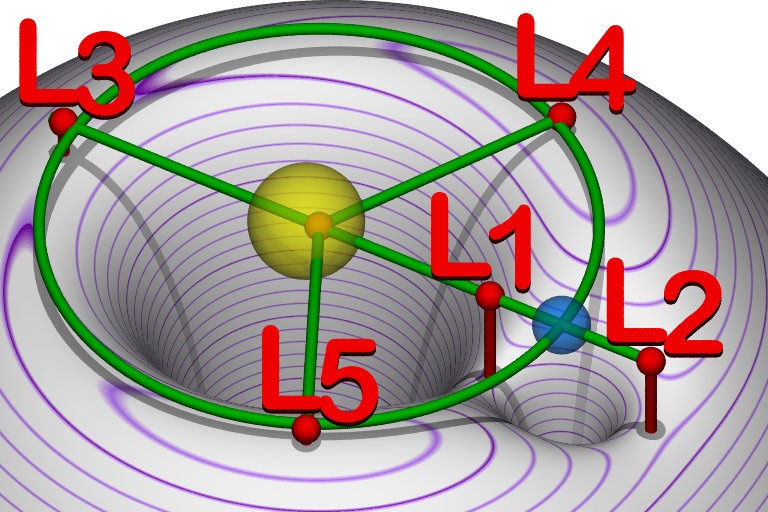
Another possibility is to locate the space station at a Lagrange point which are locations that are stable around the earth.
There are 2 sets of 5 Lagrange points. One set is associated with the Earth moon system. The other 5 are associated with the Sun Earth.
The Earth/Moon Lagrange points 4,5 are about 300,000 miles from Earth or not much different than the moon. The Sun / Earth Lagrange points are up to 100 million miles from Earth at certain times and within 1 million miles at other times.
I mention the 2 Lagrange points (L4 and L5) because they have the advantage that any small drift of the space station will cause a force that drives the object located there back to the center of the Lagrange point simply because of the gravity of the 2 bodies that form the points. This makes an ideal location for large infrastructure like the space Station.
In the 3 other Lagrange points the Space Station would constantly need to be adjusted and would be under constant stress to leave the Lagrange point and therefore would need fuel to keep it in the point or it would drift off faster and faster and eventually end up circling the sun most likely.
Sun-Earth Lagrange points 4 and 5 are located on the orbital path of the Earth meaning at times the space station would be 10s of millions of miles from Earth. It would be a substantial trip to get to these Lagrange points even if you left when the Earth was approaching the Lagrange point.
I don’t have good ideas why we would want to put the Space Station at these points other than they might be easy places for missions to other planets to get to compared to meeting up with the Earth. This might be very useful to save energy on more distant journeys.
Starship makes all of these options possible. Having the new Space Station located farther from Earth might be very convenient as a waypoint on longer missions.
Placing the Space Station more than 300,000 miles from Earth would put the station out of the protection of the Earth’s magnetic field and would require either additional protective measures against radiation or shorter duration stays. It would also increase the cost substantially because of the extra energy needed to move the mass of the station to this distant location.
Another possibility would be to build the station in low Earth orbit and then using raptor engines on the space station itself or Starships could be used a propulsion to move the station to the destination after it’s built.
When you think about it the space station might be the most compelling possible next project as it is big enough that significant tourism could be done to it giving participation to a much much larger number of people. It provides vastly more short term benefit and it is a convenient thing to have when thinking of the other missions below.
Commercial Efforts

SpaceX is already commercializing space in a major way with its Starlink system. Eventually comprising 40,000 satellites layered in several orbits between 100 and 250 miles from earth these satellites will eventually provide low latency high speed internet anywhere in the world.
Elon is not an idiot. The potential income from this is spectacular since almost any form of communication can be carried on this network from anywhere in the world it could replace the communications companies of whole countries including the US. This is potentially many billions of dollars in income. It’s a bold play. But that’s not new for Musk.
Starlink is in operation today with 1400 satellites but it is eventually going to have 40,000 satellites. Starlink is already the largest the biggest satellite company in the world by a huge factor. The majority of these satellites will eventually be launched with Starship.
What is remarkable is that despite the much larger size of Starship it is more economical than Falcon and is designed for MORE reusability with faster turnaround and more robust duty cycles. Elon has taken the lessons from the Falcon and put them into Starship and doubled down. Starship is going to be cheaper than Falcon amazingly.
The biggest weakness of Starlink at this time is that it does require a ground unit to interface to the satellite not unlike the satellite antannae you see for TV satellite carriers. Today these ground units cost consumers $500 but it means this cannot replace cell phone technology. It’s just too big to carry around.
Maybe someday this will be handheld technology but until then it can’t replace cellular networks. If Wi-Fi service became more ubiquitous with connection to Starlink you could eliminate most need for cellular service. The money that Elon makes from Starlink is undoubtedly intended to fund his more ambitious plans for Mars and other space plans.
Many people have thought of using space to commercialize everything from manufacturing some medical or materials or to mine asteroids. Those remain speculative and unclear. Elon has already targeted the main possible income from space that I am aware of.
Several other companies are trying to build Starlink competitors but they suffer from the incalculable disadvantage compared to SpaceX which owns the rockets that operate at 1/50th the cost of other launch systems. I really don’t see how they can compete and succeed against StarLink. It doesn’t seem like a fair competition.
Moon

It is 250,000 miles away which keeps it in the protection of the magnetic field of the Earth.
It is a 2 or 3 day trip compared to 9 months to Mars. The delay in talking to someone on the moon is less than a 1/4 of a second compared to 4 to 10 minutes on Mars.
NASA is already considering returning to the moon. The Artemis program has already been commissioned with SpaceX getting a $2.9 billion contract to go to the moon again.
Once again this plan is pathetic in its scope. It is unclear what the goal of this is but a moon base could do the following:
- Provide a refueling point and resupply for craft on more distant missions with a cheap low gravity well to land and lift off from
- The ability to manufacture methane for spacecraft refueling
- relatively cheap alternative for a colony and safer because of lower levels of radiation and closer to the Earth.
- Could be a processing place for asteroid missions in lieu of a space station
As far as I know Artemis does not do any of these things.
In many ways a moon base is probably a slightly cheaper version of building a space station.
It is easy to imagine that it would be possible to have a colony of hundreds of people on the moon that could do things similar to a space station.
It seems relatively safer to build a base on a stable planet than in the middle of space but it’s not clear what the advantages are to doing this on the moon vs building a space station in open space.
You can probably tell I’m not that excited about this but if the plans were more elaborated and more ambitious I could get more excited.
The fact is Starship is so cheap that many of these ideas could be done simultaneously.
Mars
Starship enables the plans I have developed for bootstrapping a colony on Mars.
My plan envisages delivering between 15-20 million lbs of stuff to Mars to achieve lift off of a largely self-supporting colony in 15 years. This would require 50-100 Starship missions.
One of the key prerequisites to doing any manned program to Mars requires something like the Starship to deliver the large mass required to support any eventual manned mission.
However, as I point out time after time a lot of the other pre-requisite technology needed to build a colony IS CURRENTLY NOT BEING DONE BY ANYBODY INCLUDING SPACEX.
To have a colony on Mars we eventually have to do the following things:
- Be able to autonomously build stuff on Mars
- including power systems, and power distribution
- GPS and high speed communications satellites
- warehouses,
- farms,
- Safe habitats for living and working,
- chemical processing
- Exploration and mapping of the planet and its resources and life
- Mining and construction robots
- processing of materials
- Manufacturing facilities
These all must be designed from scratch from the bottom up to operate in the Martian environment. Virtually nothing can be taken as is from the Earth today and delivered to Mars and be useful.
Until we see NASA, countries, companies or whoever starting to plan and build all this stuff the dream of occupying the moon or mars is a joke.
If we do not do this stuff we are in a perpetual state of delivering everything a colony needs from the Earth which is so costly that eventually we would give up and decide the whole thing was a huge waste of money.
I repeat I am opposed to the current lame and non-visionary plans of NASA. Elon has to push NASA to scale up their current plans to use Starship to do awesome things that are eminently possible now.

If we don’t get serious about doing this stuff above and NASA or SpaceX or China or somebody doesn’t step up to the plate then talk of going to Mars is fantasy and should be fantasy because it will be stupid. I see no point of going to any of these planets just to go and put boots on the ground which is what NASA and other space agencies have contemplated heretofore.
Another potential project for Starship would be to build a magnetic shield for Mars. This is not as crazy as you might think. We could place a device or devices that could provide a magnetic field in front of Mars in such a way that we shield Mars or a portion of Mars from the extreme radiation it normally gets. Doing this would greatly reduce the problems of living on Mars and may produce other positive effects.
Some have suggested that if Mars has a magnetic field the planet would spontaneously start to rebuild it’s atmosphere and eventually warm up. This might take hundreds of years and might be only partial but it could have 2 purposes. To provide a shield and as the first step in terraforming mars to eventually make it more habitable for humans.
Outer Planets

Starship enables missions that could eventually send man or our experiments far beyond earth orbit, the moon or Mars. If we put an outpost on Mars we essentially create a place where missions to the outer planets can stop, rest, refuel, resupply and then proceed on the way to longer mission.
As I’ve already pointed out Starship has the ability to deliver fuel and supplies at waypoints like Mars and other points that would allow us to plan manned missions that were much bigger. We could easily plan a mission to Jupiter.
Jupiter is twice the distance from the sun than Mars. That means an additional 12 months travel time or nearly 2 years from the Earth. Using nuclear propulsion instead of rockets like Starship could shorten this substantially but so far nuclear rockets are out of scope.
If we just look at Starship it alone makes possible such 2 year missions by allowing us to pre-position supplies to enable these journies.

As I pointed out in the space station idea above the need for rotation for longer missions becomes more and more necessary the longer the mission. Therefore being able to build rotating space structures would be necessary. So, why not build a rotating space station if we have to build rotating space craft.
You can’t launch rotating craft from Earth directly because they are not aerodynamic structures and they are too large. You have to build them in space from components delivered from multiple Starship launches.
So, ultimately to go to Jupiter and maybe even longer term travel to Mars would be via craft built entirely in space and designed to rotate rather than being launched from Earth directly. These craft could use nuclear propulsion possibly in addition to chemical thrust.
The likely supply points would be the moon, Mars, Lagrange points, or even potentially additional sun orbiting stations that would be loaded up with supplies.
Saturn and Uranus are twice the distance roughly than Jupiter and would require using Jupiter as a supply point. Eventually we might want to have a station in Jupiter orbit or on a moon of Jupiter.
New Telescopes
Many other missions to explore other parts of our solar system are possible but the closest most likely large science project would be the building of a massive telescope that would be 10-100 times the size of the Webb telescope that will be launched in a few months.
It is entirely feasible to build a telescope that is orders of magnitude bigger than Webb by using essentially a large number of Webbs and stitching together the images.
The resolving power of a telescope like this composed of 100 Webb like telescopes would enable us to actually see planets around some of the closest star systems from Earth and to explore in vastly more depth the universe and to find habitable planets around many of the star systems within 50 to 500 light years from Earth which is the most likely planets we would ever be able to go to or communicate with.
Since we can’t travel to these planets this is the most practical way for us to learn about the region of space that surrounds us before we have the capability to go there.
Other Science
One of the things many scientists get really excited about Starship is that it enables delivery of science experiments to other planets much more cheaply because of the lower cost of lift but also because they can build heavier more capable and powerful experiments.
Today exploration of the solar system has to be done by objects that weigh no more than 1,000lb on earth. This drastically limits the science and increases the costs and reduces the durability of everything.
Being able to deliver 100,000lb science experiments to Jupiter would enable mind bending kinds of capabilities. Many more experiments and equipment to do things.
Think of the helicopter we deliver to mars. Imagine instead of this wiry incredibly small helicopter we could deliver much larger flying or traversing equipment for going around on moons of the outer planets. Rovers on Jupiter’s moons with huge power sources from thermoelectric sources that could last 50 years or longer and actually traverse on those planets and run numerous experiments explore and dig below the surface.
This is just the start of the ideas people might develop once they have the ability to deliver much larger objects and in more timely and cheap manner.

Asteroids
NASA has long considered the idea of exploring asteroids and eventually mining them for materials. The financial feasibility of this is yet to be determined.
Potentially of course these asteroids contain vast quantities of rare materials that may be very valuable.
Starship makes it possible to consider exploring many asteroids economically and then potentially transporting the materials from these asteroids or the equipment needed to mine or change the orbit of these asteroids to eventually bring them into closer proximity to the Earth.
We could also develop very powerful asteroid deflection capability to provide an asteroid shield for Earth that could deflect the kind of asteroids that could end all life on Earth or huge death.
Building the Manned long distance Starship that can go on long distance potentially interstellar missions

Starship can’t violate basic physics. It’s not a ship that could allow us to go beyond our current solar system. It is not an interstellar craft. To do that will require an entirely different propulsion system and much differently designed spaceships.
Starship is powerful but it has limited fuel and cargo capacity. Therefore we require many missions to accomplish any larger objective but it is so much more powerful than what we have today it makes new much more comprehensive ideas possible.
Another thing Starship enables is the building of other more long distance craft. Starship could enable building the craft that could take us to the stars because such a ship would have to built IN SPACE not on Earth. (You can’t launch such a ship from Earth)
Starship does not make human transport any easier. There is no “human part” of Starship. Falcon has a module called the Dragon 2 which supports transport of up to 7 people.
The cargo bay of Starship is very large and would allow building a much larger human module but it does not currently have any such module.
Starship is limited to chemical propulsion which provides very high specific impulse which is good to escape large gravitational bodies like Earth but it is very inefficient for travel in space itself for longer trips. What works in Space is lower specific impulse thrust that lasts much longer like Ion or nuclear propulsion.
The weight of the chemicals for this kind of propulsion is very high for short duration. That produces lower amounts of delta V than is needed to efficiently get around our solar system. That’s why you need to have resupply depots everywhere to make it practical to get to more distant goals using Starship.
Summary

Starship is one of those completely unexpected developments that changes everything.
We shouldn’t think of Starship as simply a cheaper alternative to launch satellites or a workhorse for science missions.
Starship makes the dream that humans could be a space faring civilization real.
It’s truly spectacular achievement.
The development of the Starship requires the US and the rest of the world to upgrade and dramatically scope up our plans for space.
Should we build a new rotating space ship?
Should we plan a manned trip to Jupiter?
Should we start the effort to colonize Mars?
Should we start to plan the development of an ultra telescope 100 times bigger than the Webb?
Starship demands we think about such plans because it makes them affordable and possible.
Leave a comment